In recent years, cloud computing has become a central element of digital transformation, helping organizations innovate and scale efficiently. With advancements in cloud technologies, businesses now have the flexibility to choose between public, private, or hybrid cloud solutions. Among these, the hybrid cloud has emerged as one of the most sought-after approaches for businesses looking to combine the best of both worlds: the scalability of the public cloud and the control and security of the private cloud.
In this article, we will explore why hybrid cloud is considered the future of IT infrastructure, examining its core benefits, challenges, and why it is becoming the preferred choice for businesses across various industries. We will also address some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about hybrid cloud and summarize the key takeaways from this evolving trend in IT infrastructure.
Key Takeaways
- Flexibility and Scalability: Hybrid cloud offers businesses the ability to scale resources efficiently while maintaining control over sensitive data.
- Cost Efficiency: By combining private and public cloud resources, hybrid cloud provides a cost-effective way to manage workloads.
- Data Security and Compliance: Hybrid cloud ensures sensitive data stays protected while benefiting from the public cloud’s agility.
- Improved Disaster Recovery: Hybrid cloud offers robust disaster recovery capabilities, ensuring minimal downtime and business continuity.
- Vendor Flexibility: Hybrid cloud helps businesses avoid vendor lock-in by supporting multi-cloud strategies.
- Innovation and Future-Proofing: Hybrid cloud allows companies to embrace new technologies without disrupting existing infrastructure.
What is Hybrid Cloud?
Before diving into why hybrid cloud is the future, let’s define it clearly.
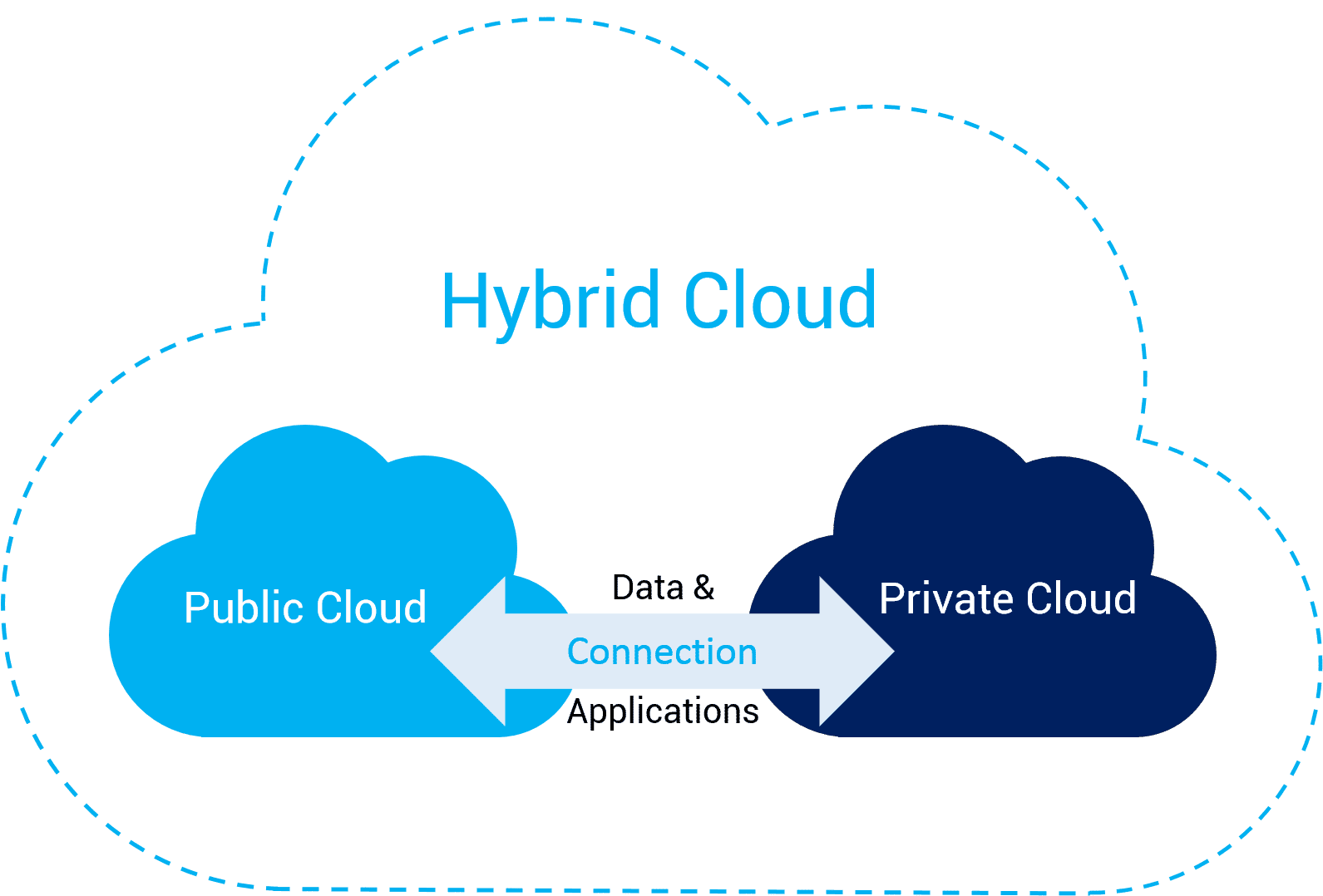
A hybrid cloud is an IT environment that combines on-premises data centers, private cloud services, and public cloud platforms to enable data and application portability, orchestration, and optimization. This allows businesses to manage workloads across both private and public cloud environments, providing greater flexibility and deployment options.
Essentially, hybrid cloud is an interconnected architecture that allows organizations to distribute workloads according to specific needs—running sensitive operations in a private cloud while leveraging the scalability and cost-effectiveness of a public cloud for less critical applications.
Why is Hybrid Cloud the Future of IT Infrastructure?
1. Flexibility and Scalability
One of the most compelling reasons why hybrid cloud is seen as the future of IT infrastructure is its inherent flexibility. In a hybrid cloud model, organizations can choose the best environment for each application or workload. Critical data and applications that require high security or compliance can be kept within the private cloud, while non-sensitive operations can scale effortlessly using the public cloud.
The scalability offered by hybrid cloud is another key factor in its growing popularity. Organizations can easily expand their capacity by offloading workloads to the public cloud as demand grows, without worrying about over-investing in physical infrastructure.
2. Cost Efficiency
Cost optimization is a major driver of hybrid cloud adoption. By maintaining a private cloud for core, sensitive workloads and using the public cloud for less critical tasks, businesses can optimize their spending. Public cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer pay-as-you-go models, meaning companies only pay for the resources they use, avoiding the upfront costs of building or expanding physical infrastructure.
Hybrid cloud gives organizations the opportunity to use both on-premises and public cloud resources efficiently, striking a balance between managing costs and leveraging advanced capabilities.
3. Data Security and Compliance
Hybrid cloud allows businesses to maintain strict control over sensitive data while benefiting from the advantages of the cloud. By keeping critical data within a private cloud or on-premises, organizations can comply with regulations and maintain tighter security controls. At the same time, non-sensitive operations can benefit from the agility and scalability of the public cloud.
For industries that require stringent compliance standards, such as healthcare, finance, and government, hybrid cloud enables the ability to meet regulatory demands while still benefiting from the public cloud’s vast infrastructure.
4. Improved Disaster Recovery

In a hybrid cloud environment, businesses can implement a robust disaster recovery (DR) strategy. Since hybrid cloud enables replication of data and applications between both private and public clouds, companies can ensure that their data is securely backed up and recoverable in case of a failure.
This redundancy across cloud environments ensures minimal downtime and faster recovery times, making hybrid cloud an ideal solution for organizations with high availability needs.
5. Enhanced Performance and Latency Reduction
Hybrid cloud allows businesses to strategically place workloads closer to end users. For example, data-intensive applications can be run on-premises or in a private cloud, while less intensive tasks can be run in the public cloud. This reduces latency and improves overall performance.
By using edge computing and hybrid cloud strategies, organizations can enhance user experience by ensuring faster access to applications, especially in cases where proximity to users is critical, such as in real-time applications or content delivery networks.
6. Future-Proofing IT Infrastructure
As technology continues to evolve, businesses must remain adaptable to new trends and tools. Hybrid cloud infrastructure allows companies to integrate new technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Internet of Things (IoT), without overhauling their existing infrastructure. This makes it easier to incorporate new innovations while maintaining legacy systems.
By offering interoperability and flexibility, hybrid cloud acts as a bridge to future technological advancements, ensuring that IT infrastructure is always capable of supporting next-gen technologies.
7. Vendor Lock-In Avoidance
A significant concern for organizations adopting cloud solutions is vendor lock-in—the dependency on a single cloud provider’s services, tools, and pricing structures. Hybrid cloud allows businesses to mitigate this risk by enabling them to switch between multiple public cloud providers or move workloads between their private and public environments as needed.
This flexibility reduces reliance on one vendor and allows organizations to take advantage of the best tools and services available from different cloud providers, ensuring they get the most competitive pricing and innovative solutions.
8. Innovation and Collaboration
Hybrid cloud fosters an environment of innovation, enabling businesses to experiment with new tools, platforms, and strategies without disrupting their existing operations. This is particularly beneficial for organizations that need to rapidly adapt to market changes, test new features, or collaborate with partners who may have different IT infrastructure needs.
Organizations can quickly deploy new cloud-native applications, integrate with external cloud services, and collaborate across geographies, all while leveraging the security and control offered by private cloud environments.
Why is Hybrid Cloud the Future of IT Infrastructure?
Now that we understand the basics of hybrid cloud, let’s dive into why it is the future of IT infrastructure.
1. Flexibility in Workload Management
One of the primary reasons why hybrid cloud is gaining traction is the flexibility it offers. Organizations are often faced with workloads that vary in their requirements—some demand high security, while others need to be processed quickly or scaled on-demand. A hybrid cloud approach provides the necessary flexibility to place workloads in the optimal environment.
- Private cloud: For workloads that require high security, such as handling sensitive customer data, financial records, or compliance-related tasks, businesses can store and process data in a private cloud environment. Private clouds offer full control over infrastructure, allowing businesses to enforce specific security policies and compliance standards.
- Public cloud: For non-sensitive tasks, like running basic applications or processing large amounts of unstructured data, businesses can utilize public cloud services, which offer a broad array of cost-effective services with infinite scalability.
This level of flexibility in workload management makes hybrid cloud an appealing choice for businesses of all sizes.
2. Cost Optimization and Efficiency

In a traditional on-premise environment, businesses must make significant capital investments in infrastructure—servers, storage, networking hardware, and more. These investments can become burdensome, especially when the infrastructure is underutilized. Public cloud providers, on the other hand, offer a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to scale their infrastructure up or down based on demand.
With a hybrid cloud model, businesses can strike a balance between private and public clouds. They can store and process critical data on private infrastructure, avoiding public cloud costs for sensitive workloads, while leveraging the public cloud’s scalability for other tasks.
For example:
- Public cloud: For less critical applications such as testing or temporary projects, businesses can leverage the public cloud and pay only for what they use. As a result, they avoid the costs of maintaining infrastructure and resources that may not be fully utilized.
- Private cloud: For applications that need to remain in-house due to regulatory, compliance, or data privacy concerns, organizations can maintain these in their private cloud infrastructure, which provides more predictable costs.
This strategic approach allows organizations to optimize costs by selecting the right platform for each workload.
3. Enhanced Security and Compliance
Hybrid cloud solutions provide businesses with enhanced security and compliance capabilities, which are critical for industries handling sensitive data. Hybrid cloud environments allow organizations to keep critical data in private clouds while taking advantage of the agility and cost-efficiency of public clouds for less-sensitive workloads.
Some of the security advantages of hybrid cloud include:
- Data isolation: Critical business data can remain isolated and controlled within private cloud environments, ensuring that sensitive information is protected from external threats.
- Compliance: For industries that must adhere to strict compliance regulations, such as healthcare (HIPAA), finance (PCI DSS), and government (GDPR), hybrid cloud provides the flexibility to store sensitive information in a secure private cloud, ensuring compliance while still enabling access to scalable computing resources in the public cloud.
Additionally, hybrid cloud providers implement robust encryption, monitoring, and access control to ensure that both private and public clouds are secure.
4. Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Hybrid cloud solutions offer significant advantages for disaster recovery and business continuity. Traditional on-premise disaster recovery strategies can be expensive and inefficient, as they require duplicated hardware and data replication efforts across different locations.
With hybrid cloud, businesses can ensure that data and applications are continuously available even in the event of a system failure or disaster. Data can be replicated in the public cloud, and workloads can be quickly migrated between environments to maintain uptime and ensure minimal disruption.
The ability to quickly switch between cloud environments is especially important for businesses that require high availability and near-zero downtime, such as e-commerce platforms, financial institutions, and service providers.
5. Optimized Performance and Reduced Latency
Hybrid cloud also provides improved performance and latency reduction, which is crucial for businesses that require real-time data processing, analytics, or low-latency applications.
- Edge computing: By placing workloads closer to end-users and using edge computing technologies, hybrid cloud can reduce latency for real-time applications. Businesses can deploy edge nodes that handle local data processing while still having access to cloud-based resources when needed.
- Geographical distribution: Public cloud providers have a vast network of data centers around the world. Hybrid cloud allows businesses to leverage the geographical distribution of cloud providers, optimizing performance by ensuring that workloads are placed closer to the end-user.
This makes hybrid cloud ideal for businesses operating on a global scale, where performance and speed are essential to user experience.
6. Future-Proofing IT Infrastructure
In an era of rapid technological change, businesses must remain agile to stay competitive. Hybrid cloud provides a pathway to future-proofing IT infrastructure by allowing businesses to adopt new technologies seamlessly while maintaining their existing infrastructure.
For instance, organizations can incorporate artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and Internet of Things (IoT) into their hybrid cloud environments. These technologies often require powerful computing capabilities that public clouds can provide. At the same time, businesses can maintain legacy applications and on-premise data storage for tasks that don’t yet require cloud scalability.
As new technologies continue to evolve, hybrid cloud allows organizations to adapt to innovations without overhauling their entire infrastructure, ensuring that they stay ahead of the curve.
7. Avoiding Vendor Lock-In
Vendor lock-in is a significant concern when adopting public cloud services. It can be difficult to migrate data or workloads from one cloud provider to another due to proprietary technologies or contractual constraints. Hybrid cloud reduces this risk by providing organizations with the flexibility to use multiple cloud providers or shift workloads between private and public clouds based on changing business needs.
By avoiding vendor lock-in, businesses can:
- Take advantage of competitive pricing.
- Select the best cloud services for specific needs.
- Avoid being restricted by the limitations of any single vendor.
8. Better Resource Allocation and Efficiency
Hybrid cloud architectures also enhance resource allocation and efficiency. By managing workloads across both private and public clouds, organizations can allocate resources more effectively. For example, workloads that require constant processing power can run in a private cloud with dedicated resources, while fluctuating workloads can be dynamically scaled to the public cloud when demand spikes.
This dynamic allocation of resources helps organizations optimize computing power, ensuring that they only use the resources they need when they need them. This elasticity is key in reducing overall operational costs while still maintaining the ability to meet high performance and availability needs.
With cloud management platforms and tools that enable real-time analytics and workload Optimization, hybrid cloud environments can ensure the most efficient allocation of resources across all layers of the cloud infrastructure.
Also Read : Why Should Your Business Adopt Cloud Computing Services?
Conclusion
The hybrid cloud model has revolutionized IT infrastructure by offering businesses a flexible, scalable, and secure way to manage their IT resources. By combining the benefits of public and private clouds, hybrid cloud allows organizations to optimize their operations, reduce costs, enhance security, and future-proof their IT strategies. It is clear that hybrid cloud is not just a passing trend but a long-term solution that will shape the future of IT infrastructure
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between a hybrid cloud and multi-cloud?
A hybrid cloud combines both private and public cloud environments, often with the ability to move workloads between the two. In contrast, multi-cloud refers to the use of multiple cloud providers (both public and private) without the direct integration between them. A hybrid cloud architecture is designed to integrate and coordinate workloads, while multi-cloud simply refers to using multiple services without deep integration.
Can small businesses benefit from hybrid cloud?
Yes, small businesses can benefit from hybrid cloud, especially when they need to balance cost control with security and scalability. Hybrid cloud allows small businesses to start with a private cloud for sensitive data and scale to the public cloud as their computing needs grow.
What are the challenges of implementing hybrid cloud?
Common challenges include complexity in managing multiple environments, security risks associated with integrating different platforms, and the need for specialized knowledge and skills to manage hybrid infrastructure. Additionally, businesses must ensure proper integration of public and private cloud systems to maintain operational efficiency.
Is hybrid cloud more secure than public cloud?
Hybrid cloud offers greater security than a purely public cloud by allowing businesses to keep sensitive data and critical applications in a private cloud while taking advantage of the scalability of the public cloud. However, security still depends on the measures implemented by the organization and the cloud providers.
What industries are most suited for hybrid cloud?
Industries that deal with sensitive data or require strict regulatory compliance—such as healthcare, finance, and government—benefit most from hybrid cloud solutions. These industries need to ensure data privacy and security while also embracing the scalability and flexibility of cloud computing.
How do hybrid clouds help with disaster recovery?
Hybrid clouds offer disaster recovery by allowing businesses to replicate data and applications across private and public cloud environments. In case of a system failure, businesses can quickly recover their workloads from the public cloud, ensuring minimal downtime and business continuity.
How does hybrid cloud help with cost savings?
Hybrid cloud allows businesses to optimize costs by leveraging the cost-effective scalability of public clouds for non-sensitive workloads while keeping critical workloads in private clouds to control expenses related to data storage and security.