Cloud integration has become a vital part of the digital transformation of businesses, organizations, and industries across the globe. In simple terms, cloud integration involves connecting cloud-based systems, applications, and services with on-premises infrastructure or other cloud services to enable seamless data flow and processes. By bridging the gap between various platforms, cloud integration ensures a unified, efficient, and scalable environment for companies to run their operations smoothly.
As businesses increasingly adopt cloud technologies to meet their needs for flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency, the demand for cloud integration solutions has skyrocketed. Whether it’s integrating cloud-based applications, connecting enterprise systems, or unifying data sources, cloud integration plays a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency and driving innovation.
In this article, we’ll explore the concept of cloud integration, its benefits, types of integration strategies, challenges involved, and best practices for successful cloud integration.
Key Takeaways
- Cloud integration connects cloud-based services, applications, and on-premises systems for seamless data exchange and collaboration.
- It offers significant benefits, including cost savings, improved efficiency, scalability, and better customer experiences.
- Businesses should follow best practices such as selecting the right tools, ensuring data consistency, and focusing on security for successful integration.
- Cloud integration can be challenging, particularly regarding security, platform compatibility, and resource management.
- With proper planning and execution, cloud integration can drive business growth and innovation.
What Are the Key Components of Cloud Integration?
Cloud integration is a multi-faceted process that involves different components to ensure smooth connectivity between various systems and platforms. Below are the essential components of cloud integration:
1. Cloud Integration Platforms (CIPs)
Cloud integration platforms are software tools or services that provide a centralized environment to manage and integrate cloud-based applications, on-premises systems, and third-party services. They facilitate data synchronization, system communication, and process automation across multiple platforms. Popular examples of cloud integration platforms include MuleSoft, Dell Boomi, and Zapier.
2. Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
APIs are the backbone of cloud integration. They enable different applications or systems to communicate with each other by providing a set of rules for data exchange. APIs facilitate the integration of cloud applications, enabling them to work together seamlessly.
3. Middleware Solutions
Middleware refers to software that connects different applications, services, or databases, enabling them to interact efficiently. In cloud integration, middleware helps manage communication between disparate systems and streamlines data exchange across the cloud and on-premises infrastructure.
4. Data Integration Tools
Data integration tools are used to extract, transform, and load (ETL) data from different sources into cloud environments. These tools are essential for ensuring data consistency and accuracy when integrating various cloud platforms or on-premises systems.
How Does Cloud Integration Benefit Businesses?
Cloud integration offers several advantages to organizations by enhancing productivity, reducing costs, and providing greater flexibility. Here are some key benefits:
1. Improved Data Accessibility
One of the main advantages of cloud integration is the ability to centralize and access data from different sources. By connecting multiple cloud-based systems, applications, and databases, businesses can have a unified view of their data. This improves decision-making and enhances business intelligence by providing real-time insights.
2. Cost Savings
Cloud integration reduces the need for on-premises infrastructure and manual interventions. By automating data flow and processes between various cloud-based systems, businesses can lower operational costs and improve resource utilization.
3. Enhanced Collaboration
With cloud integration, teams across different locations can access and share data seamlessly. This facilitates collaboration by ensuring that all stakeholders are working with the same, up-to-date information. Integration tools often include collaboration features that allow teams to work on shared projects and documents in real-time.
4. Scalability
Cloud integration makes it easier for businesses to scale their operations as needed. Since cloud platforms offer flexible and elastic resources, companies can adjust their infrastructure and services in response to changing demands without facing significant costs or delays.
5. Increased Efficiency and Automation
Automating workflows through cloud integration reduces the need for manual intervention. Data exchange, system updates, and other repetitive tasks can be automated, allowing businesses to operate more efficiently and focus on higher-value activities.
6. Improved Security
With cloud integration, businesses can enhance data security by utilizing encryption, access control, and secure APIs. Cloud providers often implement strict security measures, making it easier to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of data.
7. Better Customer Experience
Cloud integration enables businesses to provide a more personalized and streamlined experience for their customers. By integrating customer data across various touchpoints (such as CRM systems, customer support platforms, and e-commerce sites), companies can better understand their customers’ needs and deliver targeted, timely solutions.
What Are the Types of Cloud Integration Strategies?
Cloud integration strategies vary depending on the specific needs and objectives of the organization. There are several types of cloud integration approaches, each with its strengths and use cases:
1. Point-to-Point Integration
Point-to-point integration connects two systems directly, facilitating data exchange between them. This approach is often used when integrating two cloud-based applications or connecting on-premises systems with the cloud. However, as businesses scale and introduce more systems, this approach can become difficult to manage.
2. Hub-and-Spoke Integration
In a hub-and-spoke model, a central “hub” system connects multiple “spoke” systems, ensuring that each system communicates with the hub. This approach simplifies integration management by providing a single point of control for all systems involved.
3. Middleware Integration
Middleware integration uses middleware software to act as an intermediary between multiple applications or services. The middleware ensures that data flows smoothly between different systems, even if they use different protocols or technologies. This approach is ideal for complex integrations involving legacy systems or diverse platforms.
4. Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)
An ESB is a type of middleware that provides a centralized communication channel between various applications. It enables systems to exchange data and services by using standard protocols and formats, making it easier to manage integrations in a large-scale enterprise environment.
5. API-based Integration
API-based integration relies on APIs to connect different applications and systems. This approach is ideal for cloud-based integrations, as APIs offer a standardized method for communication between services. Many businesses use API management platforms to streamline and secure their API-based integrations.
What Are the Challenges of Cloud Integration?

While cloud integration provides many benefits, it also comes with its challenges. Here are some of the common issues businesses may face when implementing cloud integration:
1. Data Security and Privacy Concerns
When integrating cloud applications and services, sensitive data is often transferred between multiple systems. Ensuring data security and compliance with regulations like GDPR can be challenging, particularly when data is stored across multiple locations and providers.
2. Complexity in Managing Multiple Platforms
As businesses adopt more cloud services and applications, managing multiple cloud platforms can become increasingly complex. Cloud integration requires careful planning, monitoring, and coordination between different systems to ensure data consistency and prevent disruptions.
3. Lack of Standardization
Cloud integration often involves working with different technologies, protocols, and data formats. The lack of standardization across platforms can make it difficult to ensure compatibility between systems, leading to integration challenges.
4. Cost Management
While cloud integration can reduce costs, it can also lead to unexpected expenses. Integrating multiple cloud systems can result in hidden fees for data transfer, API usage, and additional tools. Organizations must carefully monitor costs to avoid budget overruns.
5. Downtime and Service Disruptions
Integrating cloud systems can cause temporary disruptions in services, particularly if the integration process is not carefully managed. Businesses must plan for potential downtime and ensure that backup systems are in place to minimize service interruptions.
6. Lack of Skilled Resources
Cloud integration requires expertise in cloud platforms, APIs, middleware solutions, and data management. Finding skilled professionals who can effectively manage the integration process may be challenging for some organizations.
Best Practices for Cloud Integration
To successfully integrate cloud services and platforms, businesses should follow these best practices:
1. Define Clear Objectives
Before starting the integration process, businesses should clearly define their objectives and desired outcomes. Whether it’s streamlining workflows, improving customer experiences, or optimizing costs, a clear vision will guide the integration process.
2. Choose the Right Integration Tools
Selecting the right cloud integration tools is essential for ensuring seamless integration. Businesses should evaluate different platforms based on factors such as scalability, ease of use, security, and compatibility with existing systems.
3. Ensure Data Quality and Consistency
Maintaining data quality and consistency across integrated systems is critical. Businesses should implement data validation processes and monitor data flows to ensure that all systems are using accurate and up-to-date information.
4. Focus on Security
Data security should be a top priority during cloud integration. Businesses should implement encryption, authentication, and access control measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or breaches.
5. Monitor and Optimize Integration Performance
Once the integration process is complete, businesses should continuously monitor the performance of their integrated systems. Regular monitoring helps identify any issues and provides opportunities for optimization.
6. Test Integration Before Full Deployment
Before going live with the integration, businesses should thoroughly test the integration to identify potential problems. Testing ensures that data flows correctly and that the integrated systems function as expected.
Understanding the Role of APIs in Cloud Integration
- What Are APIs?
APIs are fundamental to cloud integration, enabling different software applications to communicate and share data. This section can explore what APIs are, how they function, and their importance in enabling cloud-to-cloud and cloud-to-on-premises integration. - Types of APIs
Discuss the various types of APIs used in cloud integration, such as RESTful APIs, SOAP APIs, Web APIs, and GraphQL, explaining when and why each might be used in a cloud ecosystem. - API Management Platforms
Look into tools such as Apigee, AWS API Gateway, and Kong that help businesses manage their API integrations securely and efficiently. - Challenges and Best Practices for API Integration
Highlight common issues faced while integrating APIs, such as latency, security vulnerabilities, and scalability challenges, and provide best practices for mitigating these risks.
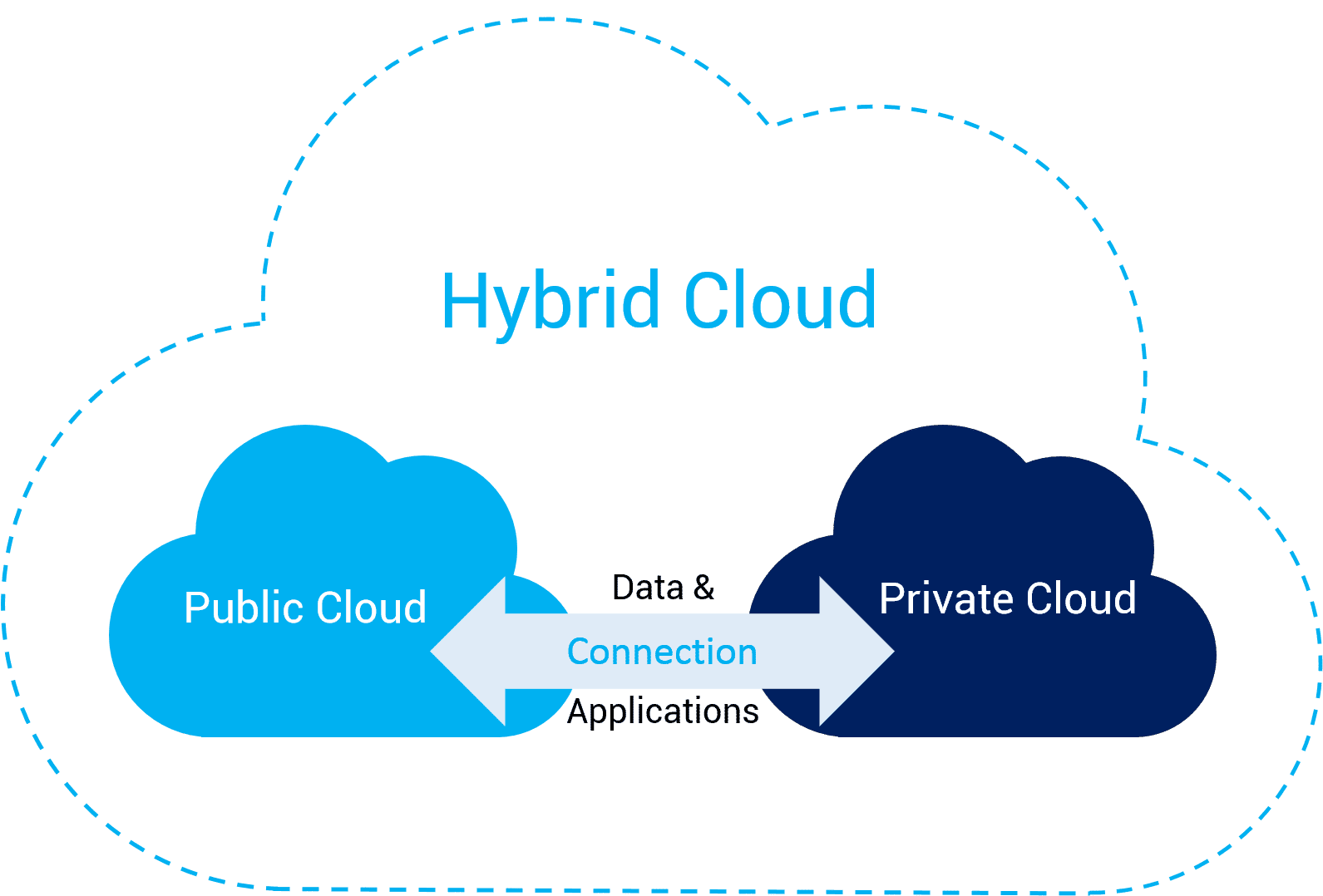
Cloud Integration in Hybrid Cloud Environments
- What is Hybrid Cloud?
Define hybrid cloud and explain how it combines private and public clouds to optimize resource utilization. - Integration Challenges in Hybrid Environments
Discuss the complexities involved in hybrid cloud integration, including compatibility, security, data management, and network configurations. - Tools for Hybrid Cloud Integration
Explore tools that facilitate integration between private and public clouds, such as Red Hat OpenShift, VMware Cloud Foundation, and Microsoft Azure Arc. - Best Practices for Hybrid Cloud Integration
Provide actionable strategies for ensuring a seamless hybrid cloud integration, focusing on security, monitoring, and compliance.
Cloud Data Integration: Techniques and Tools
- What is Cloud Data Integration?
Explore what cloud data integration entails, including the synchronization and migration of data between on-premises and cloud-based environments. - ETL vs. ELT
Compare the traditional ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) approach with ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) for cloud data integration, emphasizing the differences in process flow and performance benefits. - Data Integration Tools
Highlight leading cloud data integration tools, such as Talend, Informatica, SnapLogic, and Fivetran, discussing their features, use cases, and advantages for businesses. - Handling Big Data in Cloud Integration
Discuss how cloud integration supports the growing need for handling big data, and explore how services like AWS Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Azure Synapse Analytics help manage large datasets.
Cloud Integration and DevOps: A Synergistic Approach
- DevOps in the Cloud
Define DevOps and explain how cloud computing enhances DevOps by enabling continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and automating cloud infrastructure management. - The Role of Cloud Integration in DevOps
Explore how cloud integration facilitates collaboration between development and operations teams by providing a unified platform for code deployment, testing, and monitoring. - Automation and CI/CD in Cloud Integration
Discuss the role of tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI, and AWS CodePipeline in automating the cloud integration process for DevOps pipelines. - Best Practices for Integrating DevOps with Cloud Services
Offer a guide to best practices for using cloud services in a DevOps context, focusing on automation, version control, testing, and deployment.
Cloud Integration Security: Best Practices for Protecting Data
- Understanding Cloud Security
Explore the essential aspects of cloud security, including the shared responsibility model between cloud service providers and clients. - Security Risks in Cloud Integration
Examine the potential security risks that arise from cloud integration, such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and data loss, and discuss how to mitigate these threats. - Encryption and Access Control
Discuss encryption strategies for ensuring data protection in transit and at rest, along with implementing strong access controls (e.g., IAM, MFA). - Compliance Standards and Regulatory Requirements
Explore how cloud integration aligns with various compliance standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2, and provide insights into how businesses can meet regulatory requirements.
The Future of Cloud Integration: Trends and Innovations
- AI and Machine Learning in Cloud Integration
Investigate how artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming cloud integration by enabling intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and real-time decision-making. - Serverless Computing and Cloud Integration
Explore the rise of serverless architectures and how they impact cloud integration. Discuss how serverless computing eliminates the need for managing infrastructure and reduces overhead costs. - Edge Computing and Cloud Integration
Analyze the growing trend of edge computing, where data is processed closer to the data source, and its implications for cloud integration, especially in IoT and real-time data processing scenarios. - Cloud Integration in Multi-Cloud Environments
Discuss the trend of using multiple cloud providers (multi-cloud strategy) and the integration challenges it presents, along with solutions for managing multi-cloud environments.
Cloud Integration for Enterprises: Challenges and Solutions
- Challenges in Enterprise Cloud Integration
Highlight specific challenges faced by large enterprises during cloud integration, such as dealing with legacy systems, managing multiple cloud vendors, and addressing security concerns. - Cloud Integration in ERP Systems
Discuss how enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, such as SAP and Oracle, integrate with cloud platforms to streamline business operations, improve reporting, and enhance decision-making. - Scalable Solutions for Enterprise Cloud Integration
Provide insights into scalable solutions and tools designed for large enterprises to ensure seamless integration across vast networks of systems and applications. - Case Studies
Present real-world examples of large enterprises successfully implementing cloud integration to overcome challenges and achieve business goals.
Cloud Integration for Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs)
- Cloud Adoption in SMBs
Explore the specific needs and challenges SMBs face when integrating cloud technologies, including budget constraints, lack of technical expertise, and the need for quick deployment. - Cloud Integration Solutions for SMBs
Highlight affordable, scalable cloud integration solutions tailored for SMBs, such as low-code/no-code platforms and cloud-native integration tools. - Cost Management Strategies for SMBs
Discuss how SMBs can manage cloud integration costs while ensuring they get maximum value from their cloud investments.
Cloud Integration in Healthcare: Managing Patient Data Across Platforms
- Healthcare Data Integration
Explore how cloud integration is being used in healthcare to connect disparate systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs), laboratory systems, and appointment management platforms. - HIPAA Compliance in Cloud Integration
Discuss the importance of ensuring HIPAA compliance when integrating healthcare data across cloud platforms, focusing on security, privacy, and data handling. - Telemedicine and Cloud Integration
Examine the role of cloud integration in the growth of telemedicine, connecting healthcare providers, patients, and medical devices for better remote healthcare delivery.
Cloud Integration for eCommerce: Enhancing Customer Experience
- Integration of eCommerce Platforms
Discuss how eCommerce platforms like Shopify, Magento, and WooCommerce integrate with various cloud services (e.g., payment gateways, shipping services, CRM systems) to enhance customer experience. - Real-time Data Synchronization in eCommerce
Explain the importance of real-time data synchronization across various eCommerce channels, such as inventory, pricing, and order management, to provide a seamless shopping experience. - Cloud Integration for Personalized Customer Interactions
Explore how cloud-based data integration supports personalized marketing, product recommendations, and customer support in eCommerce.
The Economic Impact of Cloud Integration: Cost-Effectiveness and ROI
- Cost Optimization Through Cloud Integration
Discuss how cloud integration helps reduce costs by optimizing cloud resource usage, minimizing downtime, and automating processes. - Return on Investment (ROI) from Cloud Integration
Analyze the potential ROI of cloud integration for Businesses, considering both tangible benefits (cost savings, increased revenue) and intangible benefits (improved efficiency, customer satisfaction). - Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in Cloud Integration
Explore the concept of TCO in cloud integration, including upfront costs, ongoing operational costs, and hidden fees.
Also Read : What Are The Top Cloud Computing Technologies For Data Security?
Conclusion
Cloud integration is a crucial step for businesses looking to maximize the potential of their cloud technologies and improve overall operations. By ensuring that systems, applications, and data sources work together seamlessly, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, scalability, and collaboration. However, the process also comes with challenges, including data security, complexity, and cost management. To succeed, businesses should adopt best practices, such as defining clear objectives, choosing the right integration tools, and continuously monitoring performance.
FAQs
1. What is cloud integration?
Cloud integration refers to the process of connecting different cloud-based services, applications, or systems with each other or with on-premises infrastructure to enable data exchange, automation, and collaboration.
2. Why is cloud integration important for businesses?
Cloud integration allows businesses to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, reduce costs, improve scalability, and provide better customer experiences by unifying data and systems.
3. What are the types of cloud integration?
There are several types of cloud integration strategies, including point-to-point integration, hub-and-spoke integration, middleware integration, ESB-based integration, and API-based integration.
4. What are the benefits of cloud integration?
Cloud integration offers benefits such as improved data accessibility, cost savings, enhanced collaboration, scalability, increased automation, and better customer experiences.
5. What challenges come with cloud integration?
Challenges in cloud integration include data security concerns, managing multiple platforms, lack of standardization, cost management, downtime risks, and the need for skilled resources.
6. How can businesses ensure successful cloud integration?
Businesses can ensure successful cloud integration by defining clear objectives, choosing the right integration tools, ensuring data quality, focusing on security, and continuously monitoring and optimizing integration performance.
7. What is an API-based integration?
API-based integration involves using application programming interfaces (APIs) to connect different systems and applications, allowing them to communicate and exchange data in a standardized manner.